PUBLICATION TITLE:
A prospective, first-in-human use of the NeVa mechanical thrombectomy device for patients with acute coronary syndromes
Authors:
Alessandro Spirito, MD; Angelo Quagliana, MD; Marco Coiro, MD; Gebremedhin D. Melaku, MD; Stijn Vandenberghe, MD; Gregor Leibundgut, MD, PhD; Jonas Häner, MD; Marco Moccetti, MD; Marco Araco, MD; Hector M. Garcia-Garcia, MD; Marco ValgimigliJournal:
Eurointervention, Feb 2021Background:
There is no established technique for managing large thrombus burden (LTB) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).Methods:
- enVast was used for primary vessel recanalization and thrombus removal, followed by conventional intervention
- A subset of patients received vacuum-assisted aspiration as an adjudicative manoeuvre
- Procedural complications, TIMI flow, MBG, and TTG were core-lab reviewed
aim:
Between Nov. 2019 & Mar.2021, 61 consecutive acute coronary syndrome patients with large thrombus burden underwent thrombectomy with the enVast device to assess its safety and efficacy.
Results:
TIMI Flow
- enVast deployment was associated with immediate reperfusion in 85% and TIMI-3 flow in 74% of the patients with TIMI-0 after wire insertion
- TIMI-3 flow increased from 31.7% to 90% after enVast (p<.001)
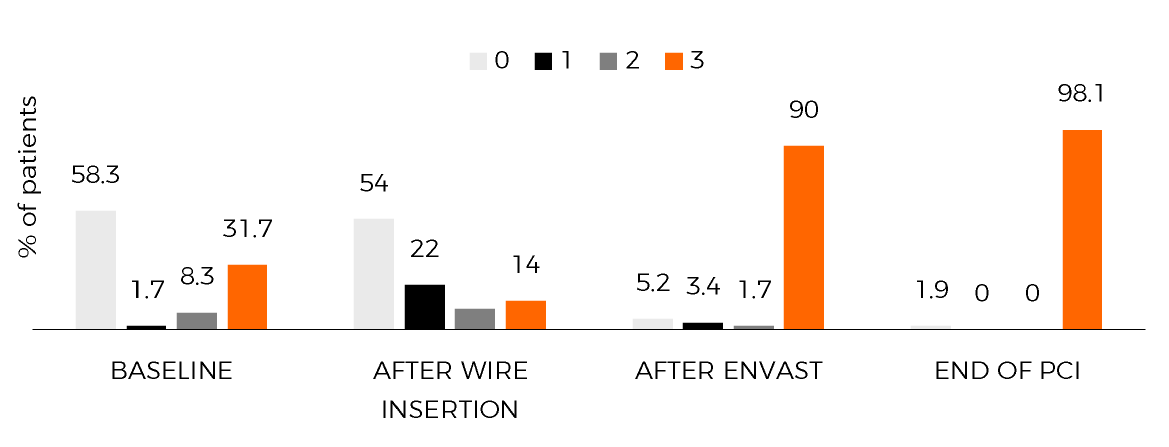
ST ELEVATION RESOLUTION
- STE Resolution (≥50%) in 71.7% of patients
- Complete STE REsolution (≥70%) in 43.5% of patients
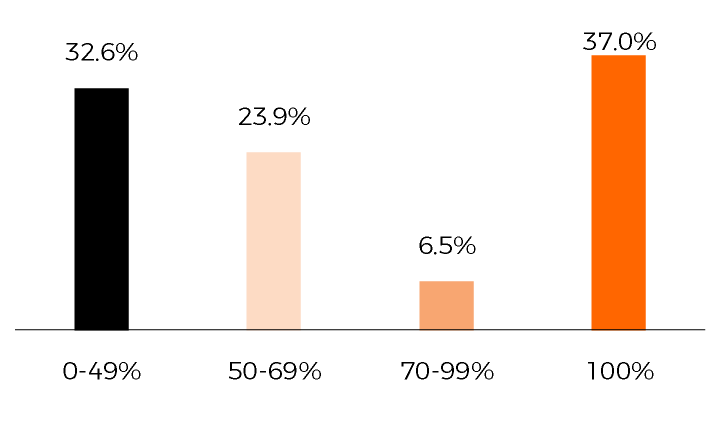
TIMI THROMBUS GRADE
- enVast retrieved macroscopic thrombotic material in 53% of the cases
- enVast use decreased the angiographic thrombus burden to ≤2 in 56.9% of the patients (p<.001)

MYOCARDIAL BLUSH GRADE
- MGB 0-1 was detected in 65% of patients at baseline and in 27% after enVast use(p<.001)
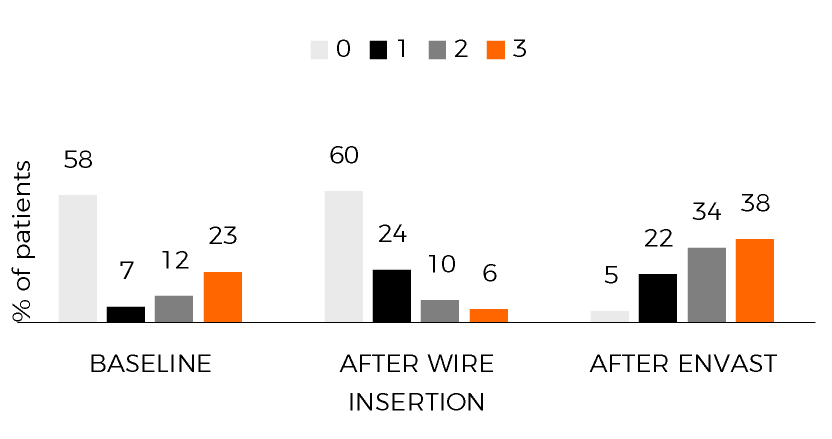
Safety:
- Non-flow limiting, reversable coronary spasm: 14 patients (23%)
- Side branch embolization in 1 successfully treated patient (#10): triggered the development of vacuum-assisted co-aspiration technique, which was then applied to the subsequent 51 patients
- No other device-related complications occurred